Data quality for unstructured data
Dec 2025
Authors

Hrishabh Gokhru
Senior Consultant, Cloud & Data Tech


Rahul Jadhav
Senior Consultant, Cloud & Data Tech


Ankur Gupta
Senior Consultant, Cloud & Data Tech

Subeer Sehgal
Principal Consultant, Cloud & Data Tech


Sonal Sudeep
Principal Consultant, Cloud & Data Tech
Executive summary
In today’s data-driven enterprises, ensuring data quality for both structured and unstructured data has become essential yet challenging. Traditionally, data quality initiatives focus on structured data like spreadsheets and databases, but often neglect unstructured data such as emails, PDFs, and images. Unstructured data accounts for nearly 80% of enterprise data today, and maintaining its quality is a major challenge. Poor quality in unstructured data compromises analytics accuracy, elevates compliance risks, and hampers operational efficiency. This paper highlights the strategic importance of unstructured data quality and proposes a comprehensive framework to address these issues effectively.
Introduction
Context and background: Organizations are increasingly relying on unstructured data for advanced analytics, machine learning, and decision-making. Unlike structured data stored in relational databases, unstructured data lacks a predefined schema, making it harder to validate, cleanse, and standardize. Sources such as social media feeds, customer emails, IoT sensor logs, and multimedia files contain valuable insights but also introduce complexity due to volume, variety, and veracity. As businesses move toward data-driven strategies, ensuring the quality of unstructured data becomes critical for maintaining trust, compliance, and competitive advantage.
Current challenges: Despite its growing importance, unstructured data presents unique challenges for data quality management:
Variations in document layouts and formats: Multiple templates for similar content hinder standardization.
Difficulty linking to business data: Unstructured content does not align seamlessly with relational systems.
Frequent changes in source structure: Layout changes break existing extraction processes.
Duplicate and outdated versions: Multiple versions across systems confuse.
Incomplete or low-quality source files: Poor scans and noisy audio reduce extraction accuracy.
Lack of consistent metadata: Files are mislabeled or lack proper tags, complicating retrieval and lineage tracking.
Tooling limitations: Traditional data quality tools are designed for structured data and fail to address unstructured formats effectively.
Compliance risks: Sensitive information embedded in unstructured content can lead to regulatory violations if not properly managed.
To address these challenges, we propose a new framework to help manage the quality of unstructured data. The framework ensures that unstructured data, such as documents, images, audio, and video, is consistently captured, transformed, validated, and governed to meet enterprise data quality standards. It addresses challenges like inconsistent formats, missing metadata, and poor interpretability, enabling trusted insights and compliance.
Unstructured data quality management framework: From raw to reliable
IDC estimates that 80-90% of all data is unstructured, and that this figure is growing exponentially. Businesses generate petabytes of text, audio, video, and image data every year. There’s simply too much of it to manage manually. This framework provides a structured approach to capture, monitor, and validate unstructured data, ensuring it is analytics-ready and compliant.
Managing unstructured data quality requires a structured, multi-step approach that transforms raw, fragmented content into trusted, analytics-ready datasets. Our framework begins with data ingestion and validation, where files are detected through landing zones or APIs, and essential metadata such as file type, source, and timestamp is verified. This step ensures completeness and prevents duplicates or incomplete files from entering the pipeline.
The next step involves structured transformation, where advanced parsers and extraction logic are used to interpret unstructured content such as PDFs, images, and audio. Important entities and metrics are organized into standardized tables that conform to a unified data model, ensuring consistency across diverse sources. During this stage, new entity types and parsing rules are also registered to support ongoing adaptation to changing business needs. Once transformed, the data is profiled and validated for quality based on criteria like accuracy, integrity, interpretability, and relevancy. Automated checks detect anomalies, tag key data elements, and enforce domain-specific rules. Files that fail these checks are flagged for correction, with root cause analysis and corrective actions, such as source fixes or pipeline adjustments, taken to restore data integrity.
Finally, the framework emphasizes scalable governance and monitoring, with rule-based dashboards tracking quality scores and compliance. This ensures audit readiness, supports AI and automation initiatives, and enables rapid onboarding of new unstructured formats without major redesign.
Key dimensions for monitoring unstructured data quality
To ensure unstructured data is reliable and fit for purpose, the framework incorporates specific dimensions that measure quality across multiple aspects:
Interpretability: Focuses on how well the data can be understood and utilized. This involves profiling coverage and ensuring that essential metadata fields, such as title, description, and tags, are populated. High interpretability makes data easier to classify, search, and integrate into workflows.
Relevancy: Ensures that extracted features and entities align with domain-specific requirements. Rule-based scoring validates whether the data is contextually meaningful for the intended business use case, reducing noise and improving decision accuracy.
Accuracy: Measures the correctness of extracted data against predefined standards and validation rules. This includes format checks, valid time spans, and classifier confidence scores for tagging and feature extraction. Accurate data minimizes downstream errors and enhances trust.
Integrity: Validates relationships across records and fields, ensuring links between files, metadata, and associated objects remain intact. This dimension is critical for maintaining consistency across complex datasets such as contracts, invoices, or multimedia files.
Three-step process to convert unstructured data to structured data
The transformation approach is executed through three key stages:
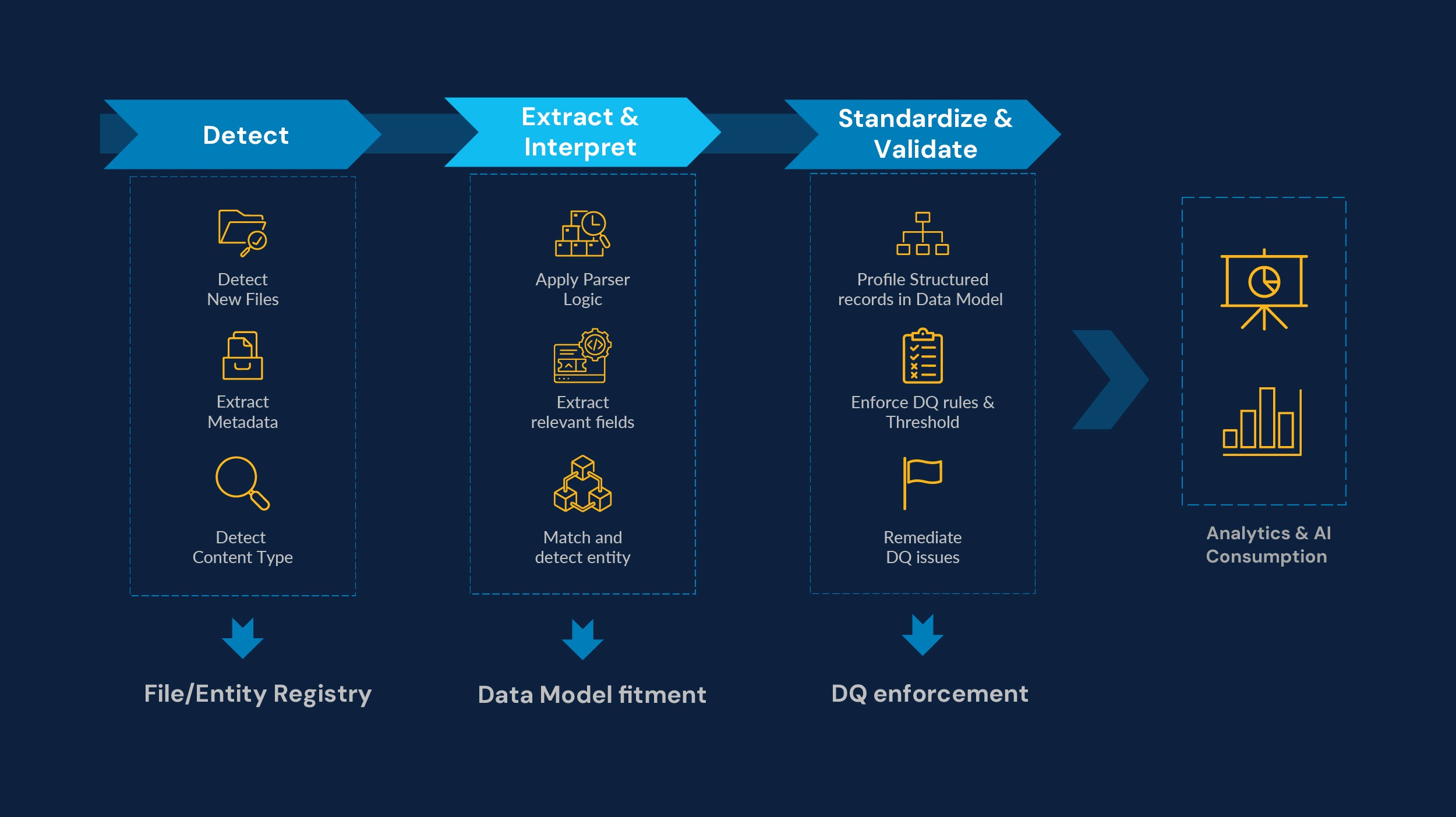
Detect: Identify new files via landing zones or APIs, validate accessibility, and extract basic metadata such as file name, size, and source. This step ensures correct content type identification (PDF, image, audio, video) and readiness for processing.
Extract and interpret: Apply parser logic and extraction rules to analyze content, extract relevant fields and entities, and match them against master data. Missing metadata is flagged, and new entities are created. Standard formats and naming conventions are applied for consistency.
Standardize and validate: Transform extracted data into structured records aligned with a unified data model. Enforce data quality thresholds, flag anomalies, and route problematic files for remediation. Store clean, validated data in target systems for analytics and AI consumption.
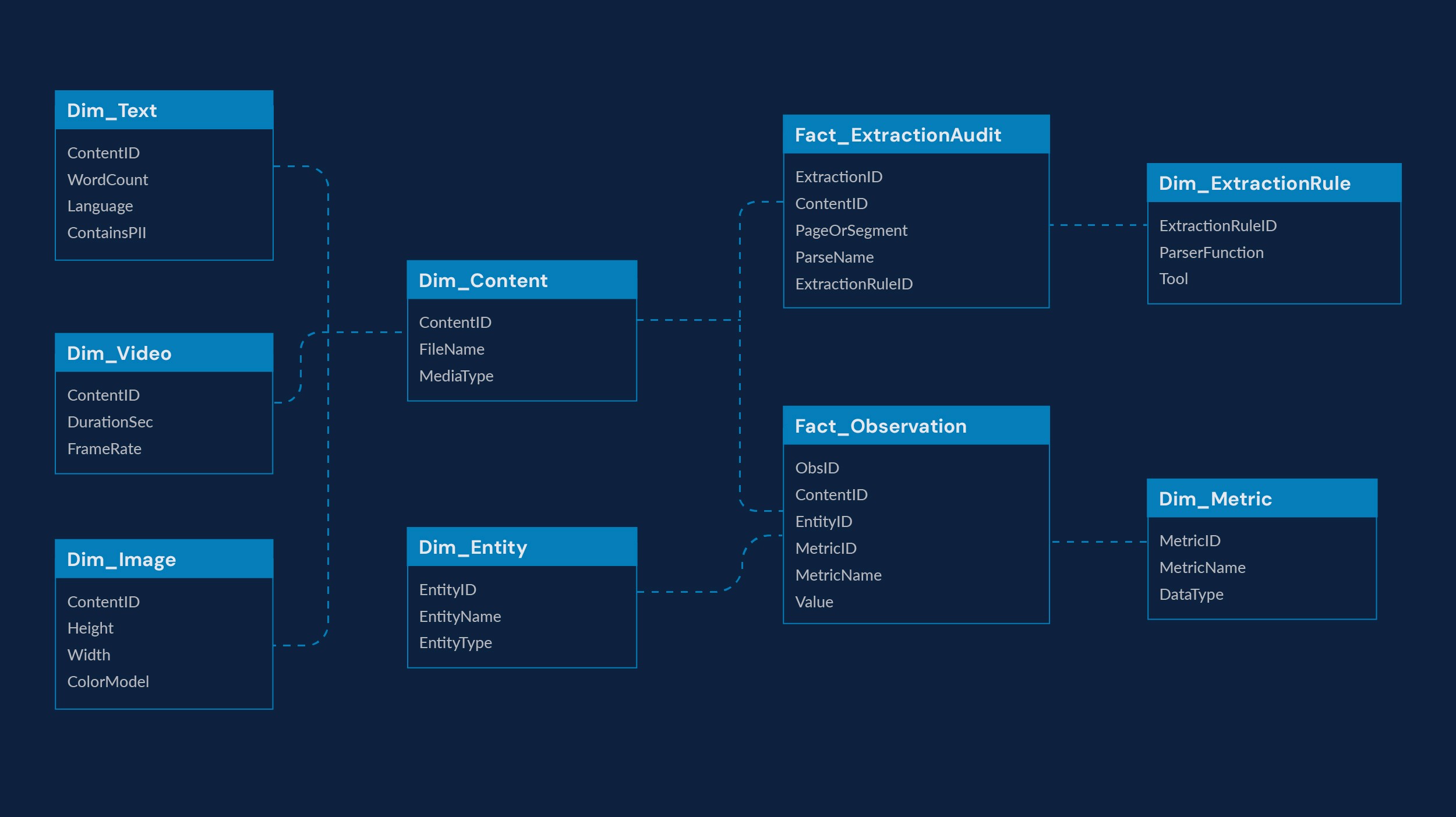
Below is an example of a data model that organizes extracted insights and metadata from processed files into a structured schema. At core, Fact_Observation stores granular insights extracted from each file and is keyed to Entity (EntityID), Metric (MetricID), and Content (ContentID). Dim_Entity, Dim_Metric, and Dim_Content define the business context, metric dictionary, and source/lineage metadata for each observation. Additional dimensions like Dim_Text, Dim_Image, and Dim_Video capture modality-specific details, while Fact_ExtractionAudit and Dim_ExtractionRule enable robust data lineage, quality governance, and traceability across the extraction process.
Conclusion
Implementing an Unstructured Data Quality Management Framework is no longer optional; it is a strategic necessity. As organizations increasingly rely on AI, automation, and advanced analytics, the ability to trust and govern unstructured content becomes critical. High-quality unstructured data unlocks business-critical insights from documents, emails, images, and audio files, enabling faster, more accurate decision-making.
By adopting this framework, businesses can achieve five key benefits:
Unlock hidden insights: Transform “dark data” into actionable intelligence that drives marketing, sales, finance, and compliance strategies.
Accelerate AI and automation: With 80% of enterprise data being unstructured, improving its quality enhances AI model accuracy and optimizes automation workflows.
Enhance customer experience: Deliver clean, structured insights from customer interactions to enable personalization and faster issue resolution, boosting customer loyalty.
Improve operational efficiency: Increase productivity through automated validation and remediation, eliminating manual rework, errors, and wasted hours spent searching for documents.
Ensure compliance and reduce risk: Maintain audit-ready lineage and governance to meet regulatory requirements, reducing compliance costs.
In short, this framework turns fragmented, inconsistent content into a trusted enterprise asset driving innovation, efficiency, and competitive advantage.
Introduction
Context and background: Organizations are increasingly relying on unstructured data for advanced analytics, machine learning, and decision-making. Unlike structured data stored in relational databases, unstructured data lacks a predefined schema, making it harder to validate, cleanse, and standardize. Sources such as social media feeds, customer emails, IoT sensor logs, and multimedia files contain valuable insights but also introduce complexity due to volume, variety, and veracity. As businesses move toward data-driven strategies, ensuring the quality of unstructured data becomes critical for maintaining trust, compliance, and competitive advantage.
Current challenges: Despite its growing importance, unstructured data presents unique challenges for data quality management:
Variations in document layouts and formats: Multiple templates for similar content hinder standardization.
Difficulty linking to business data: Unstructured content does not align seamlessly with relational systems.
Frequent changes in source structure: Layout changes break existing extraction processes.
Duplicate and outdated versions: Multiple versions across systems confuse.
Incomplete or low-quality source files: Poor scans and noisy audio reduce extraction accuracy.
Lack of consistent metadata: Files are mislabeled or lack proper tags, complicating retrieval and lineage tracking.
Tooling limitations: Traditional data quality tools are designed for structured data and fail to address unstructured formats effectively.
Compliance risks: Sensitive information embedded in unstructured content can lead to regulatory violations if not properly managed.
To address these challenges, we propose a new framework to help manage the quality of unstructured data. The framework ensures that unstructured data, such as documents, images, audio, and video, is consistently captured, transformed, validated, and governed to meet enterprise data quality standards. It addresses challenges like inconsistent formats, missing metadata, and poor interpretability, enabling trusted insights and compliance.
Unstructured data quality management framework: From raw to reliable
IDC estimates that 80-90% of all data is unstructured, and that this figure is growing exponentially. Businesses generate petabytes of text, audio, video, and image data every year. There’s simply too much of it to manage manually. This framework provides a structured approach to capture, monitor, and validate unstructured data, ensuring it is analytics-ready and compliant.
Managing unstructured data quality requires a structured, multi-step approach that transforms raw, fragmented content into trusted, analytics-ready datasets. Our framework begins with data ingestion and validation, where files are detected through landing zones or APIs, and essential metadata such as file type, source, and timestamp is verified. This step ensures completeness and prevents duplicates or incomplete files from entering the pipeline.
The next step involves structured transformation, where advanced parsers and extraction logic are used to interpret unstructured content such as PDFs, images, and audio. Important entities and metrics are organized into standardized tables that conform to a unified data model, ensuring consistency across diverse sources. During this stage, new entity types and parsing rules are also registered to support ongoing adaptation to changing business needs. Once transformed, the data is profiled and validated for quality based on criteria like accuracy, integrity, interpretability, and relevancy. Automated checks detect anomalies, tag key data elements, and enforce domain-specific rules. Files that fail these checks are flagged for correction, with root cause analysis and corrective actions, such as source fixes or pipeline adjustments, taken to restore data integrity.
Finally, the framework emphasizes scalable governance and monitoring, with rule-based dashboards tracking quality scores and compliance. This ensures audit readiness, supports AI and automation initiatives, and enables rapid onboarding of new unstructured formats without major redesign.
Key dimensions for monitoring unstructured data quality
To ensure unstructured data is reliable and fit for purpose, the framework incorporates specific dimensions that measure quality across multiple aspects:
Interpretability: Focuses on how well the data can be understood and utilized. This involves profiling coverage and ensuring that essential metadata fields, such as title, description, and tags, are populated. High interpretability makes data easier to classify, search, and integrate into workflows.
Relevancy: Ensures that extracted features and entities align with domain-specific requirements. Rule-based scoring validates whether the data is contextually meaningful for the intended business use case, reducing noise and improving decision accuracy.
Accuracy: Measures the correctness of extracted data against predefined standards and validation rules. This includes format checks, valid time spans, and classifier confidence scores for tagging and feature extraction. Accurate data minimizes downstream errors and enhances trust.
Integrity: Validates relationships across records and fields, ensuring links between files, metadata, and associated objects remain intact. This dimension is critical for maintaining consistency across complex datasets such as contracts, invoices, or multimedia files.
Three-step process to convert unstructured data to structured data
The transformation approach is executed through three key stages:
Detect: Identify new files via landing zones or APIs, validate accessibility, and extract basic metadata such as file name, size, and source. This step ensures correct content type identification (PDF, image, audio, video) and readiness for processing.
Extract and interpret: Apply parser logic and extraction rules to analyze content, extract relevant fields and entities, and match them against master data. Missing metadata is flagged, and new entities are created. Standard formats and naming conventions are applied for consistency.
Standardize and validate: Transform extracted data into structured records aligned with a unified data model. Enforce data quality thresholds, flag anomalies, and route problematic files for remediation. Store clean, validated data in target systems for analytics and AI consumption.

Below is an example of a data model that organizes extracted insights and metadata from processed files into a structured schema. At core, Fact_Observation stores granular insights extracted from each file and is keyed to Entity (EntityID), Metric (MetricID), and Content (ContentID). Dim_Entity, Dim_Metric, and Dim_Content define the business context, metric dictionary, and source/lineage metadata for each observation. Additional dimensions like Dim_Text, Dim_Image, and Dim_Video capture modality-specific details, while Fact_ExtractionAudit and Dim_ExtractionRule enable robust data lineage, quality governance, and traceability across the extraction process.

Conclusion
Implementing an Unstructured Data Quality Management Framework is no longer optional; it is a strategic necessity. As organizations increasingly rely on AI, automation, and advanced analytics, the ability to trust and govern unstructured content becomes critical. High-quality unstructured data unlocks business-critical insights from documents, emails, images, and audio files, enabling faster, more accurate decision-making.
By adopting this framework, businesses can achieve five key benefits:
Unlock hidden insights: Transform “dark data” into actionable intelligence that drives marketing, sales, finance, and compliance strategies.
Accelerate AI and automation: With 80% of enterprise data being unstructured, improving its quality enhances AI model accuracy and optimizes automation workflows.
Enhance customer experience: Deliver clean, structured insights from customer interactions to enable personalization and faster issue resolution, boosting customer loyalty.
Improve operational efficiency: Increase productivity through automated validation and remediation, eliminating manual rework, errors, and wasted hours spent searching for documents.
Ensure compliance and reduce risk: Maintain audit-ready lineage and governance to meet regulatory requirements, reducing compliance costs.
In short, this framework turns fragmented, inconsistent content into a trusted enterprise asset driving innovation, efficiency, and competitive advantage.
Recognition and achievements

Named leader
Customer analytics service provider Q2 2023

Named leader
Customer analytics service provider Q2 2023

Representative vendor
Customer analytics service provider Q1 2021

Representative vendor
Customer analytics service provider Q1 2021

Great Place to Work, USA
8th year running. Certifications received for India, USA,Canada, Australia, and the UK.

Great Place to Work, USA
8th year running. Certifications received for India, USA,Canada, Australia, and the UK.
Registered Office:
Level 7, Commerz II, International Business Park, Oberoi Garden City,Off. W. E.Highway, Goregaon (E), Mumbai City, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India, 400063
Phone: +91 22 6850 5800
Email: investorrelations@fractal.ai
CIN : U72400MH2000PLC125369
GST Number (Maharashtra) : 27AAACF4502D1Z8
Registered Office:
Level 7, Commerz II, International Business Park, Oberoi Garden City,Off. W. E.Highway, Goregaon (E), Mumbai City, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India, 400063
Phone: +91 22 6850 5800
Email: investorrelations@fractal.ai
CIN : U72400MH2000PLC125369
GST Number (Maharashtra) : 27AAACF4502D1Z8

