Utilizing data effectively sets market leaders apart. Strategic data products (SDP) transform raw data into actionable insights, driving decision-making, efficiency, and innovation. They are essential for creating new revenue streams, enhancing customer experiences, optimizing operations, and making real-time decisions.
As data volume grows, structured, reliable, and accessible SDPs are critical. Adopting a strategic approach enables businesses to harness the full potential of data, foster a data-driven culture, and maintain a competitive edge.
What are strategic data products?
SDPs are tools that use data to solve specific business problems or create new opportunities. They are crafted to be reusable and scalable; empowering organizations to derive maximum value from their data assets. Key components of SDPs include:
Reusable datasets: Curated data collections across projects streamline analytics and reduce redundancy.
Code/data models: Scripts and algorithms analyze data, from simple statistics to complex machine learning, predicting future trends.
ML/predictive models: Advanced models learn from patterns to automate decisions, helpful in predicting customer behavior and demand forecasting.
Dashboard reports:Interactive visual representations provide real-time insights and key performance indicators (KPIs), supporting informed decision-making.
To better understand SDPs, let’s look at some practical examples:
| Customer data products | Consumer data products | Manufacturing data products |
|---|---|---|
| Consolidate data from different sources for a detailed view of customer interactions, enabling personalized marketing and improved service. | Focus on broader consumer behavior and trends. Retailers use these to analyze shopping patterns and optimize inventory management. | Track and analyze production data to identify inefficiencies and predict maintenance needs, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime. |
Key properties
SDPs are fundamental to modern data strategy, turning raw data into assets that drive business growth and efficiency. To do this, they need to have the following essential properties:
Discoverability: SDPs should be easily discoverable within an organization. This means having a well-organized data catalog where users can quickly find the necessary data without sifting through irrelevant information.
Understandability: SDPs must be presented in a way that is understandable to all stakeholders, regardless of their technical expertise. Clear documentation and user-friendly interfaces help achieve this.
Trustworthiness: Trust in data is paramount. SDPs must ensure data accuracy and integrity through rigorous validation and reconciliation processes. This builds confidence among users that the insights derived from the data are reliable.
Addressability: SDPs should address specific business problems. They must be designed with a clear purpose, ensuring they bring tangible value to the organization.
Interoperability: SDPs must be compatible with various systems and platforms within the organization. This enables seamless integration and data sharing across different departments and functions.
Value: Ultimately, SDPs must provide value to the business. This could be in the form of cost savings, revenue generation, or improved operational efficiency.
Accessibility: SDPs should be accessible to those who need them when they need them. This means implementing robust access controls and ensuring data can be easily retrieved and utilized through APIs or other interfaces.
Why are strategic data products essential?
Traditional use case-specific projects incur high costs due to repeated data ingestion and analysis, leading to financial strain. Maintaining multiple siloed solutions increases maintenance costs and complexity, requiring dedicated resources for updates and bug fixes.
This approach leads to redundancy, as teams repeatedly collect and process the same data, wasting time and resources.
It also creates high technical debt, burdening organizations with outdated, inefficient systems. Siloed projects lead to data duplication, causing inconsistencies and increased storage costs. Non-standard architectures further hamper interoperability and scalability, making integrating new systems or scaling existing ones difficult.
Benefits of strategic data products
SDPs unlock new revenue by identifying cross-selling and up-selling opportunities, tailoring marketing, and launching products that meet emerging needs.
They provide real-time insights for informed decision-making, forecasting market trends, and customer behaviors. This improves resource allocation and strategic alignment within organizations.
SDPs also boost efficiency by optimizing processes, reducing waste, and predicting maintenance needs. In logistics, they enhance route planning and inventory management, resulting in cost savings and better service levels.
By dramatically speeding up insight generation through centralized, reusable data assets and automated processes, SDPs accelerate decision-making and response times. Robust data governance and quality control ensure accuracy and reliability, building user trust.
Designed for real-time data ingestion and processing, SDPs also enable timely decisions that are crucial in dynamic markets. Centralized and standardized data promotes reusability across projects, reducing redundancy and costs. Robust governance frameworks and automated monitoring enhance maintainability, easing the IT burden.
Lastly, SDPs also boost agility, allowing quick adaptation to changing business needs and the development of new features, which are essential for competitiveness in fast-paced markets.
How to build and implement strategic data products
To build effective SDPs, identify specific business problems and engage with stakeholders to define objectives, ensuring the product delivers relevant insights.
Then:
● Assign a clear owner for accountability and governance.
● Organize SDPs into domains and subdomains to align with business functions, facilitating management and relevance.
● Conduct data discovery to map sources, understand structures and assess quality, ensuring comprehensiveness and accuracy.
● Implement data quality and governance frameworks with validation rules and reconciliation processes to maintain high standards.
● Develop the product iteratively, incorporating user feedback and adapting to changing needs. Focus on creating key SDPs that offer the most value, such as customer, sales, or financial data products.
● Design a robust architecture to support efficient operation, defining data flow, storage, and integration points.
● Automate monitoring and management with alerts for quality issues, tracking data lineage, and ensuring master data management practices are in place to maintain data integrity and efficiency.
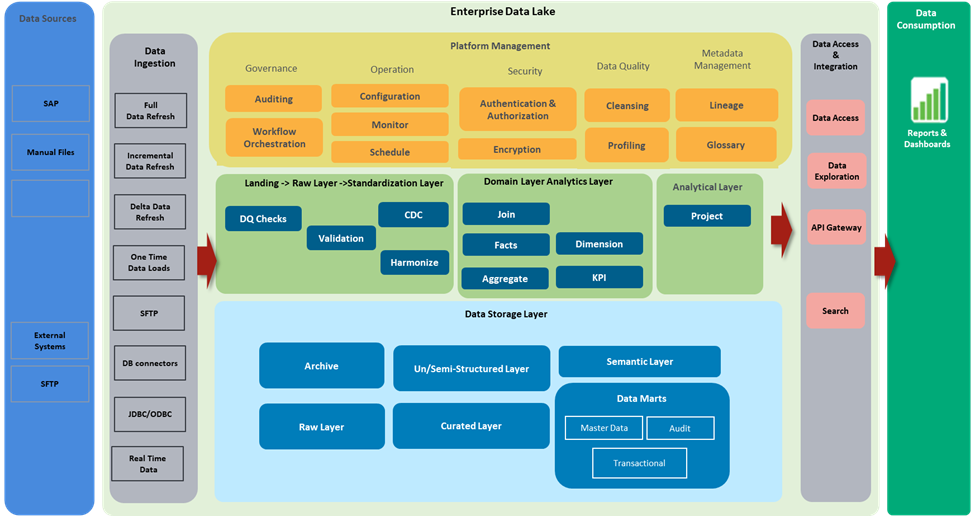
Case study: enhancing supply chain efficiency with a customer data product
A global consumer goods company faced challenges in streamlining supply chain operations due to fragmented customer data, manual processes, and limited insights into performance. These issues led to inefficiencies, delays, and errors.
We developed a customer data product that integrated data from multiple sources into a single platform. This included consolidated customer data, advanced analytics models, and interactive dashboards. Machine learning models optimized inventory levels and predicted demand. At the same time, real-time dashboards provided insights into order fulfillment and inventory status.
We identified the company’s needs and established clear ownership and governance for the data product. Data from various sources was mapped, integrated, and validated. The product was developed iteratively with continuous improvements, incorporating feedback. A robust architecture supported scalable and efficient operations, with automated monitoring ensuring performance.
The customer data product improved the accuracy of the case fill rate, enhanced customer satisfaction, and reduced penalties for missed deliveries. Automated integration and analysis saved time and minimized errors. Real-time insights enabled better inventory management and demand forecasting, while centralized data management reduced redundancy and maintenance costs.
Conclusion
SDPs are essential for organizations to leverage data effectively and maintain a competitive edge. They drive decision-making, efficiency, and innovation by transforming raw data into actionable insights. This way, new revenue streams are created, customer experiences enhanced, and operations optimized, enabling real-time decisions. As data volumes grow, the importance of structured, reliable, and accessible SDPs increases. Adopting a strategic approach to data products allows businesses to harness the full potential of data, fostering a data-driven culture and positioning themselves as leaders in a data-centric world.


